- Home
- .NET tutorials
- How to find a client's geolocation in .NET with IP lookup
How to find a client's geolocation in .NET with IP lookup
Published: Monday 1 July 2024
There may be instances when you want to serve different content to clients based on their location.
Adding geolocation to ASP.NET Core
We are going to add this to an ASP.NET Core Web API. We've set up a model that will store the geolocation of the client, such as the IP address and country name.
// GeoIpCountryModel.cs
public class GeoIpCountryModel
{
public string IpAddress { get; }
public string? CountryIsoCode { get; }
public string? CountryName { get; }
public IReadOnlyDictionary<string, string>? CountryNames { get; }
public GeoIpCountryModel(string ipAddress, string? countryIsoCode, string? countryName, IReadOnlyDictionary<string, string>? countryNames)
{
IpAddress = ipAddress;
CountryIsoCode = countryIsoCode;
CountryName = countryName;
CountryNames = countryNames;
}
}We've also set up a service where we'll write the functionality to lookup a country based on an IP address.
// IGeoIpService.cs
public interface IGeoIpService
{
GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress);
}// GeoIpService.cs
public class GeoIpService : IGeoIpService, IDisposable
{
const string IP_ADDRESS_REGEX = "^(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))$";
public GeoIpService()
{
}
public GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress)
{
return null;
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
}We'll add this to dependency injection as a singleton instance. It will become clearer later in the tutorial as to why we add this as a singleton.
// Program.cs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
// Added to dependency injection with a singleton lifetime
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IGeoIpService, GeoIpService>();
var app = builder.Build();
...
app.Run();Validate the IP address to ensure it's in the correct format
In GeoIpService, we've added a method called GetCountry which takes in the IP address as the parameter. Before we do anything, we want to ensure that it's a valid IPv4 address.
^(?:1)?(?:\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\d|5[0-5]))\.(?:1)?(?:\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\d|5[0-5]))\.(?:1)?(?:\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\d|5[0-5]))\.(?:1)?(?:\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\d|5[0-5]))$
GeoIpService to validate the IP address. The checks involve a null check before validating against the regular expression pattern.
// GeoIpService.cs
public class GeoIpService : IGeoIpService, IDisposable
{
const string IP_ADDRESS_REGEX = "^(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))$";
public GeoIpService()
{
}
public GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (!IsValidIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
return null;
}
return null;
}
private bool IsValidIpAddress(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ipAddress))
{
return false;
}
// Check format of IP address
if (!Regex.IsMatch(ipAddress, IP_ADDRESS_REGEX))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
}At this point, we are ready to do an IP lookup.
How to add IP lookup to your .NET project
We are going to use GeoLite2 from MaxMind to add IP lookup to our .NET project.
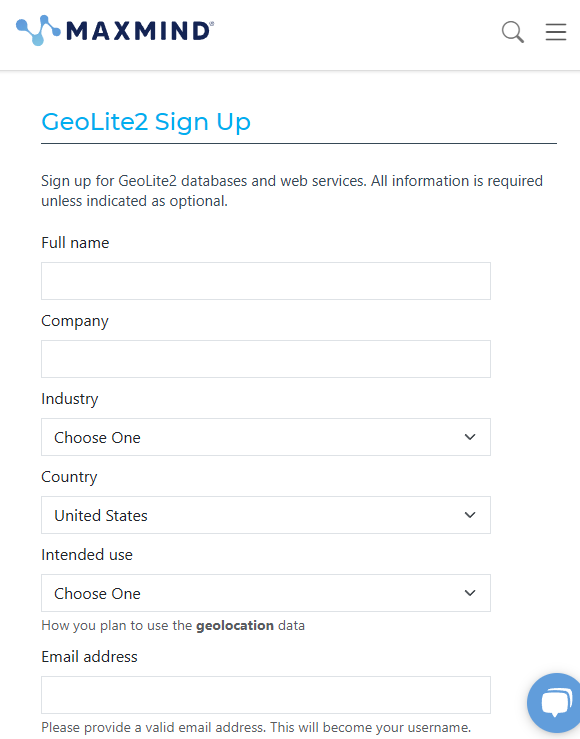
Sign up for a MaxMind account to add geolocation to your .NET project
Once you've signed up, MaxMind will send you an email allowing you to set your password.
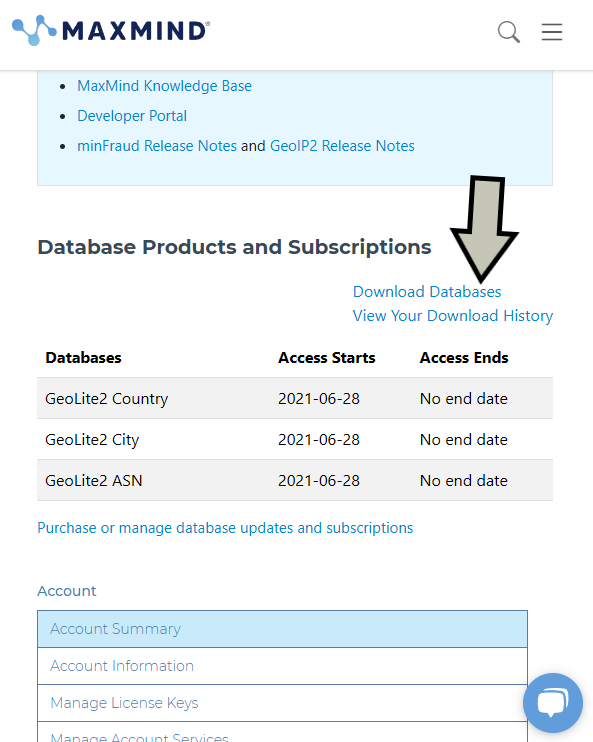
MaxMind screen allowing you to download databases
Click on the Download Databases link and you'll be greeted with a number of databases that you can download.
mmdb format, so download the GZIP for it.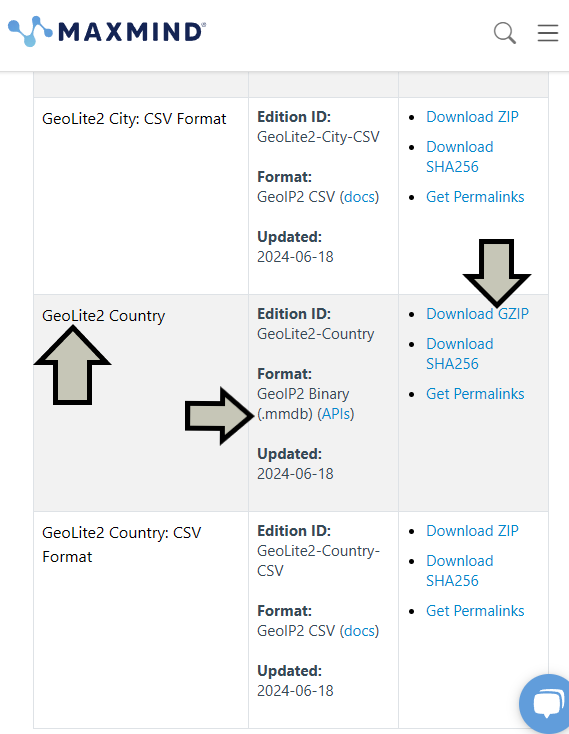
Download the GeoLite2 Country database in mmdb format
This will download a .tar.gz file. If you are unable to open these files, you can install WinRAR onto your machine.
GeoLite2-Country.mmdb file into your Web API project in a new folder called Databases.
Databases folder, click on GeoLite2-Country.mmdb and go to Properties.
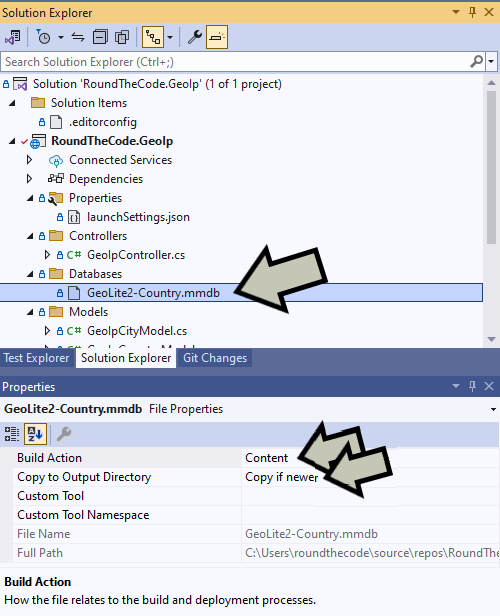
Add MaxMind GeoLite2 Country database to your ASP.NET Core Web API project
You now have the lookup database added to your ASP.NET Core Web API project.
Add the NuGet package
Before you can start using it, you need to add the MaxMind.GeoIP2 NuGet package. This will allow you to do the IP lookup using the GeoLite2 database.
Add the IP address lookup
Now that you have the NuGet package, you can read the GeoLite2 database and this is something we'll add to the GeoIpService class when it's initalised.
DatabaseReader object rather than creating a new one for each lookup as creating a new object is relative expensive on resources. This is the reason why the GeoIpService class is using a singleton instance as it will keep an instance of the DatabaseReader object for the lifetime of the application.
Path.GetDirectoryName(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location) to get the folder of where your ASP.NET Core Web API is being executed. Then simply append the location of your database to it.
DatabaseReader object is disposable, we can dispose of it when the GeoIpService class is also disposed.
// GeoIpService.cs
public class GeoIpService : IGeoIpService, IDisposable
{
private readonly DatabaseReader _countryDatabaseReader;
const string IP_ADDRESS_REGEX = "^(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))$";
public GeoIpService()
{
_countryDatabaseReader = new DatabaseReader(Path.Combine(Path.GetDirectoryName(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location), "Databases/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb"));
}
public GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (!IsValidIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
return null;
}
// Get country information from database.
return null;
}
private bool IsValidIpAddress(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ipAddress))
{
return false;
}
// Check format of IP address
if (!Regex.IsMatch(ipAddress, IP_ADDRESS_REGEX))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
_countryDatabaseReader.Dispose();
}
}To get the country based on an IP address, we can call the Country method in the DatabaseReader object, passing in the IP address as the parameter.
AddressNotFoundException. We'll need to catch that, and return null if that's the case.
GeoIpCountryModel class that we set up earlier. The properties we are going to return are:
IpAddress- The IP address that we are looking up.CountryIsoCode- The two letter ISO code for the country e.g. for the United States this would beUS.CountryName- The name of the country (in English).CountryNames- The names of the country in multiple languages, such as French and Spanish.
// GeoIpService.cs
public class GeoIpService : IGeoIpService, IDisposable
{
private readonly DatabaseReader _countryDatabaseReader;
const string IP_ADDRESS_REGEX = "^(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))$";
public GeoIpService()
{
_countryDatabaseReader = new DatabaseReader(Path.Combine(Path.GetDirectoryName(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location), "Databases/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb"));
}
public GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (!IsValidIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
return null;
}
// Get country information from database.
CountryResponse countryResponse;
try
{
countryResponse = _countryDatabaseReader.Country(ipAddress);
}
catch (AddressNotFoundException)
{
return null;
}
if (countryResponse?.Country == null)
{
return null;
}
// Return ISO country code.
return new GeoIpCountryModel(ipAddress, countryResponse.Country.IsoCode, countryResponse.Country.Name, countryResponse.Country.Names);
}
private bool IsValidIpAddress(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ipAddress))
{
return false;
}
// Check format of IP address
if (!Regex.IsMatch(ipAddress, IP_ADDRESS_REGEX))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
_countryDatabaseReader.Dispose();
}
}Testing it using a Web API controller
We are going to test this functionality using a Web API controller called GeoIpController.
// GeoIpController.cs
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class GeoIpController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IGeoIpService _geoIpService;
public GeoIpController(IGeoIpService geoIpService)
{
_geoIpService = geoIpService;
}
[HttpGet("country")]
public IActionResult GetCurrentCountry()
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCountry(HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString()) });
}
[HttpGet("country/{ipAddress}")]
public IActionResult GetCountry(string ipAddress)
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCountry(ipAddress) });
}
}We have created two endpoints.
/api/geoip/country/6.6.6.6, it returns the following JSON response:
{
"ipAddress": {
"ipAddress": "6.6.6.6",
"countryIsoCode": "US",
"countryName": "United States",
"countryNames": {
"de": "USA",
"en": "United States",
"es": "Estados Unidos",
"fr": "États Unis",
"ja": "アメリカ",
"pt-BR": "EUA",
"ru": "США",
"zh-CN": "美国"
}
}
}How to get the client's IP address when on a reverse proxy
Using HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString() works fine if you are using a standalone server.
X-Forwarded-For. This usually contains the IP address of the client.
ForwardedHeaders middleware that you can use to override the value of HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress.
Program.cs.
// Program.cs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
// Add forwarded headers middleware
builder.Services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders =
ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
});
var app = builder.Build();
...
// Use forwarded headers middleware
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
...
app.Run();This can be tested in Postman by adding a X-Forwarded-For header to the request and seeing the response.
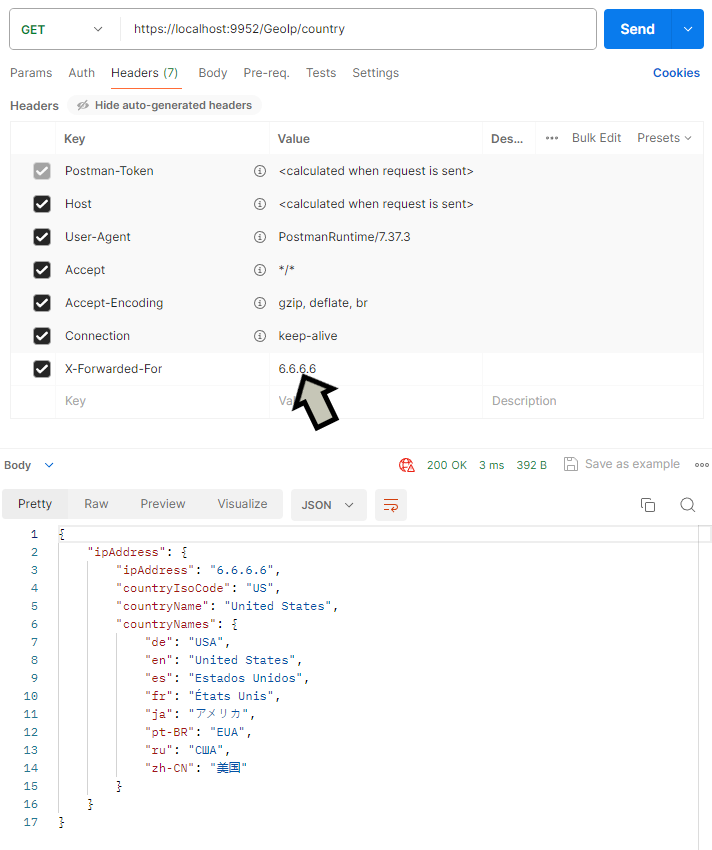
Added X-Forwarded-For to the request
Adding a custom header for the IP address
You may find that your reverse proxy adds its own request header for the client's IP address.
CF-Connecting-IP as a request header that is used as the IP address of the original request.
ForwardedHeaders middleware to add the header name by using the ForwardedForHeaderName property in ForwardedHeadersOptions.
// Program.cs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
// Add forwarded headers middleware
builder.Services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
options.ForwardedForHeaderName = "CF-Connecting-IP";
});
var app = builder.Build();
...
// Use forwarded headers middleware
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
...
app.Run();By adding CF-Connecting-IP to the request header, it now returns the country based on that IP address.
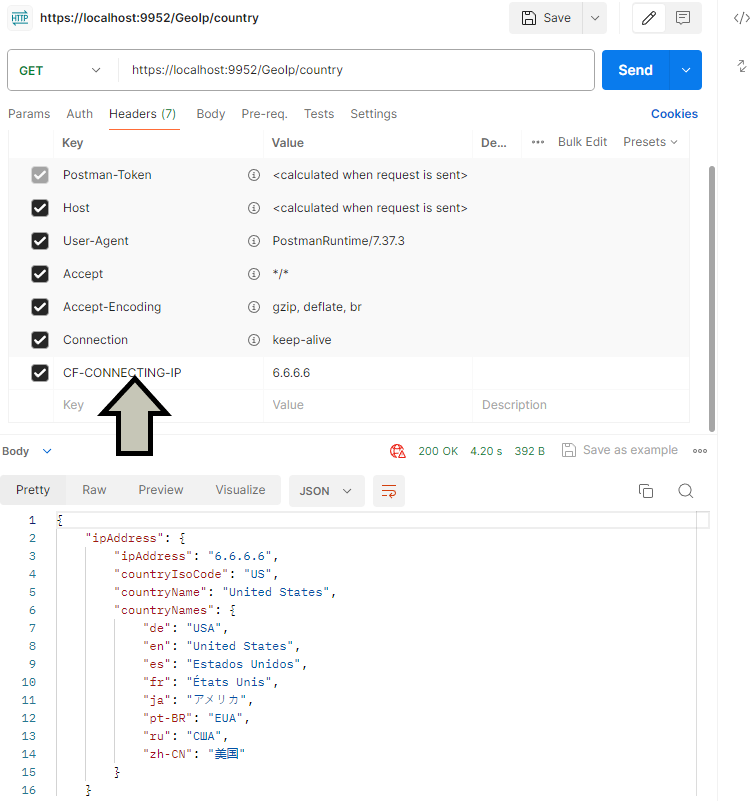
Add custom header to the request
Just an important security note to only use the ForwardedHeaders middleware if you are using a reverse proxy.
Adding the city database
GeoLite2 also comes with a separate city database. Not only does that contain the information about the country, but also about the city.
mmdb.
GeoIpService class to also include lookup for the city.
GetCity to do an IP address lookup based on the city.
// GeoIpService.cs
public class GeoIpService : IGeoIpService, IDisposable
{
private readonly DatabaseReader _cityDatabaseReader;
private readonly DatabaseReader _countryDatabaseReader;
const string IP_ADDRESS_REGEX = "^(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))\\.(?:1)?(?:\\d{1,2}|2(?:[0-4]\\d|5[0-5]))$";
public GeoIpService()
{
_cityDatabaseReader = new DatabaseReader(Path.Combine(Path.GetDirectoryName(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location), "Databases/GeoLite2-City.mmdb"));
_countryDatabaseReader = new DatabaseReader(Path.Combine(Path.GetDirectoryName(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location), "Databases/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb"));
}
public GeoIpCityModel? GetCity(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (!IsValidIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
return null;
}
// Get country information from database.
CityResponse cityResponse;
try
{
cityResponse = _cityDatabaseReader.City(ipAddress);
}
catch (AddressNotFoundException)
{
return null;
}
if (cityResponse?.City == null && cityResponse?.Country == null)
{
return null;
}
return new GeoIpCityModel(ipAddress, cityResponse?.City?.Name, cityResponse?.Country?.IsoCode, cityResponse?.Country?.Name, cityResponse?.Country?.Names);
}
public GeoIpCountryModel? GetCountry(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (!IsValidIpAddress(ipAddress))
{
return null;
}
// Get country information from database.
CountryResponse countryResponse;
try
{
countryResponse = _countryDatabaseReader.Country(ipAddress);
}
catch (AddressNotFoundException)
{
return null;
}
if (countryResponse?.Country == null)
{
return null;
}
// Return ISO country code.
return new GeoIpCountryModel(ipAddress, countryResponse.Country.IsoCode, countryResponse.Country.Name, countryResponse.Country.Names);
}
private bool IsValidIpAddress(string? ipAddress)
{
// Don't check if there is no IP address.
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ipAddress))
{
return false;
}
// Check format of IP address
if (!Regex.IsMatch(ipAddress, IP_ADDRESS_REGEX))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
public void Dispose()
{
_cityDatabaseReader.Dispose();
_countryDatabaseReader.Dispose();
}
}We can also modify the GeoIpController to test out the methods.
// GeoIpController.cs
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class GeoIpController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IGeoIpService _geoIpService;
public GeoIpController(IGeoIpService geoIpService)
{
_geoIpService = geoIpService;
}
[HttpGet("city")]
public IActionResult GetCurrentCity()
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCity(HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString()) });
}
[HttpGet("city/{ipAddress}")]
public IActionResult GetCity(string ipAddress)
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCity(ipAddress) });
}
[HttpGet("country")]
public IActionResult GetCurrentCountry()
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCountry(HttpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString()) });
}
[HttpGet("country/{ipAddress}")]
public IActionResult GetCountry(string ipAddress)
{
return Ok(new { IpAddress = _geoIpService.GetCountry(ipAddress) });
}
}Just a note that the City information in GeoLite2 isn't that accurate. When we tried it against our IP address, it thought we were based in a location around 120 miles (193 km) away from where we really are.
Latest tutorials

Swagger's missing in .NET 10 - How to add it back
Swagger is missing in .NET 10. Learn why it was removed, how to add it back, and explore alternatives like Scalar, Redoc, Postman, and .http files.

